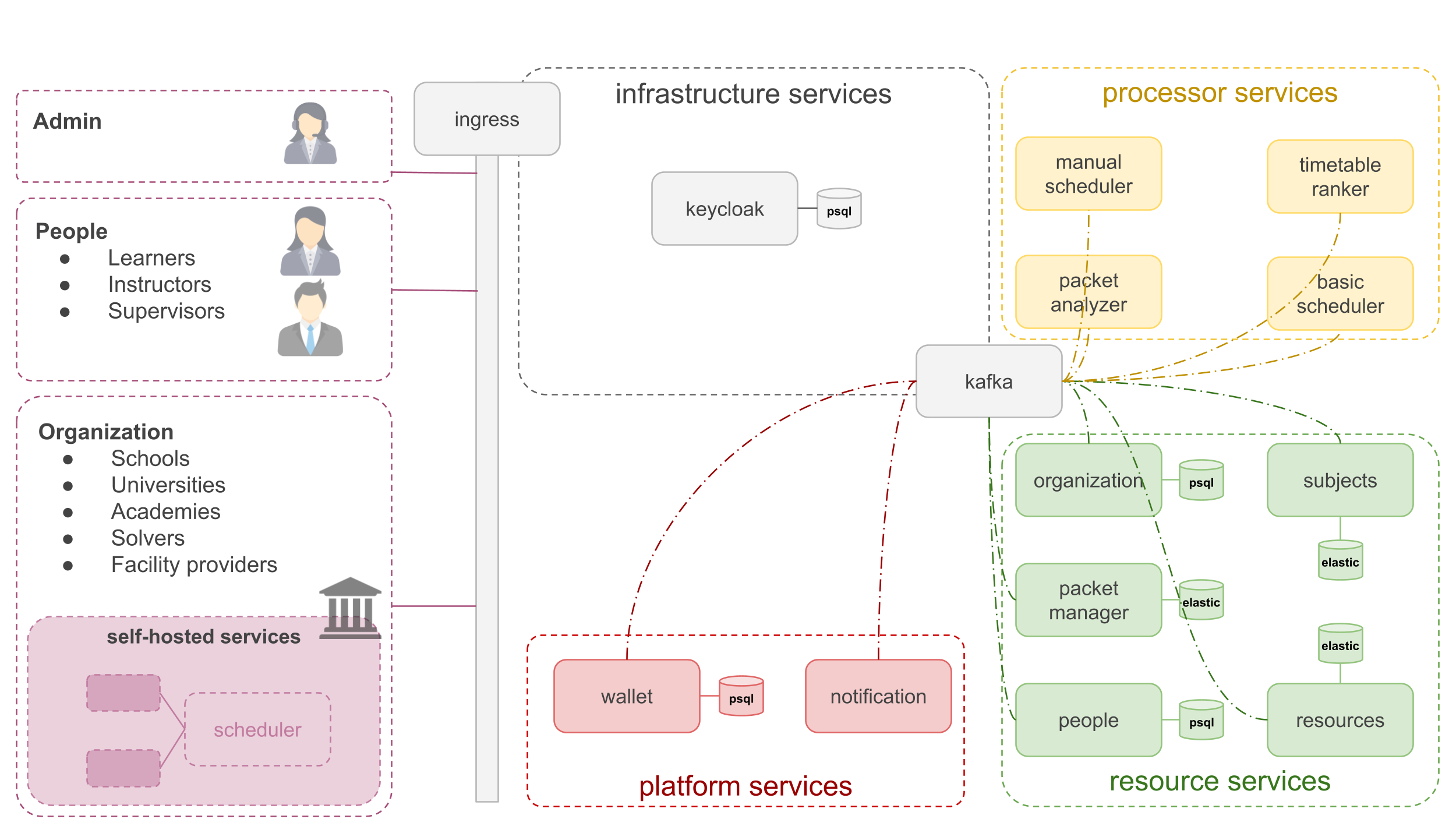
Architecture
The Distributed Timetable Assistant (DTA) is a Kubernetes-first microservices platform with clear separation of concerns: Resource Services, Processor Services, Cloud-exclusive Platform Services, and Infrastructure Services. Resource and Processor services can be run as cloud-shared services (tiered plans) or deployed self-hosted inside customer environments; cloud-exclusive services are only available from the hosted platform. The architecture uses Kafka as the central event bus, Postgres/Elasticsearch/Redis for state, and Keycloak for identity.
Service summary table
| Group | Service | Persistence / stores | Self-hostable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource services | packet-manager | Elasticsearch (primary index) | ✅ |
| people | PostgreSQL | ✅ | |
| organization | PostgreSQL | ✅ | |
| resources | PostgreSQL | ✅ | |
| subjects | PostgreSQL | ✅ | |
| Processor services | basic-scheduler | PostgreSQL + Redis | ✅ |
| manual-scheduler | PostgreSQL + Redis | ✅ | |
| Cloud-exclusive platform | wallet | PostgreSQL | ❌ (cloud-only) |
| timetable-ranker | (ephemeral & DB as needed) | ❌ | |
| packet-analyzer | (analytics store; may use ES/PSQL) | ❌ | |
| notification | PostgreSQL | ❌ | |
| Infrastructure | ingress | — | — |
| kafka | — (stateful) | — | |
| keycloak | PostgreSQL (Keycloak DB) | — |
Service details
Resource services (self-hostable / cloud-shared)
These services contain canonical domain data and publish domain events to Kafka. They are the primary candidates for customer self-hosting when data locality is required.
packet-manager
- Role: Manages timetable packets (submissions, search index, versions), stores indexed representations and search metadata.
- Persistence: Elasticsearch (primary index); may also keep metadata in PostgreSQL if needed.
- API: REST/gRPC endpoints for create/read/update/search; produces events (e.g.,
packet.created,packet.updated) to Kafka. - Deployment hints: Stateful/managed ES or operator (ECK / Opensearch operator) for reliability; replicas and index lifecycle policies required.
people
- Role: Stores learner, instructor, supervisor profiles, credentials metadata, availability calendars (links to time-blocks).
- Persistence: PostgreSQL.
- API / Events: CRUD endpoints; emits
person.created/person.updated/person.availability.changedevents to Kafka. - Self-host notes: Allow sync/backups for institutions that want to keep identity locally.
organization
- Role: Stores organization metadata (schools, universities, academies, facility providers, solver registrations).
- Persistence: PostgreSQL.
- Events:
organization.*domain events for changes in facility availability, policies, or membership.
resources
- Role: Catalog of educational materials and facility metadata (rooms, equipment), attachments or pointers to object storage.
- Persistence: PostgreSQL (metadata) and object store (S3) for large assets; may index in Elasticsearch for content search.
- Events:
resource.*events for material updates affecting scheduling.
subjects
- Role: Canonical subject definitions (e.g., “Physics 2”), mapping of subjects to curricula and competency metadata.
- Persistence: PostgreSQL.
- Events:
subject.*events used by schedulers and packet analyzers.
Processor services (self-hostable / cloud-shared)
Processors consume domain events, run scheduling logic, and publish candidates/results.
basic-scheduler
- Role: Automated timetable generator (batch/stream mode) that creates candidate timetables based on constraints and resource availability.
- Persistence: PostgreSQL (durable job / result store) + Redis (caches, distributed locks, ephemeral job state, worker queues).
- Integration: Subscribes to Kafka topics (resource updates, new packets); writes candidates back to
packet-manager(or to a results topic). - Scaling: Horizontal workers; Redis-backed queues for task distribution.
manual-scheduler
- Role: Human-in-the-loop scheduling assistant supporting GUI-based edits, conflict resolution, and confirmations.
- Persistence: PostgreSQL + Redis for ephemeral session state.
- Behavior: Accepts operator edits, publishes modifications to Kafka so ranker/notification can react.
Cloud-exclusive platform services (hosted only)
Services that the platform provides but are not part of the baseline self-host offering.
wallet
- Role: Marketplace ledger/credits management for solvers, microservices and institutions.
- Persistence: PostgreSQL (transactional ledger).
- Security: Strong auditing; integrate with external payment providers for top-ups.
timetable-ranker
- Role: Scores and ranks candidate timetables from multiple schedulers (features from packet-analyzer + telemetry).
- Persistence / storage: May use an analytics DB or cache; primary operation is stream processing of candidate events.
- Integration: Consumes candidates from Kafka, emits
candidate.rankedevents.
packet-analyzer
- Role: Feature extraction and analytics for submitted packets (complexity, conflict density, resource usage).
- Persistence: Analytical store (Elasticsearch or analytic Postgres), intermediate caches.
- Use: Feeds features to the ranker and to metric dashboards.
notification
- Role: Centralized subscription and delivery engine (email, push, SMS integrations).
- Persistence: PostgreSQL for subscription config and templates.
- Integration: Consumes events (e.g.,
candidate.finalized,wallet.balance.low) and triggers deliveries.
Infrastructure services (cluster-level)
Cross-cutting components required by all services.
ingress
- Role: Tenant-aware edge routing, TLS termination, path-based or host-based routing for self-hosted vs cloud endpoints.
- Examples: NGINX Ingress, Traefik, or a cloud load balancer.
kafka
- Role: Central event bus used for decoupling producers (resource & platform services) and consumers (processors, analytics).
- Operational: Multi-zone replication, topic retention/policy, schema registry recommended for event contracts (Avro/Protobuf).
keycloak
- Role: Identity and access management (OAuth2/OpenID Connect). Centralized realm and client configuration.
- Persistence: PostgreSQL backing store for Keycloak data.
- Notes: For self-hosted installs, allow integration with the institution’s IAM or run a local Keycloak instance.
How the pieces interact (short flow)
- Clients → Ingress → authenticated via Keycloak.
- CRUD on domain entities → Resource services (Postgres / ES) → emit domain events to Kafka.
- Processor services consume Kafka, produce candidate timetables → write results back to
packet-managerand emit ranked/candidate events. packet-analyzerandtimetable-rankerconsume streams to score and finalize selections.- Platform services (
wallet,notification) handle transactions and user communication for marketplace actions.